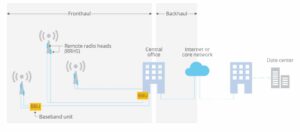
5G fronthaul networks are the backbone of high-speed, reliable 5G connections, bridging the gap between central data centres and base stations. This critical infrastructure ensures that data is efficiently transferred across various network segments, making it essential for delivering the exceptional performance that 5G promises.
Maintaining the robustness of these connections is crucial. However, several potential impairments can challenge optimal performance. This is where network impairment testing becomes indispensable. By rigorously evaluating how the network performs under various conditions, this testing helps address and mitigate these challenges effectively.
Why Network Impairment Testing Matters
Network impairment testing evaluates how well a network performs under different conditions, focusing on identifying and resolving issues that could impact service quality, such as:
- Identifying Weak Spots: Testing helps pinpoint specific areas where the network may be underperforming or failing. This could include issues like signal degradation, latency (delays in data transmission), or interference from other signals.
- Ensuring Reliability By replicating different scenarios and stress conditions, testing ensures that the network can handle various loads and interruptions. This is vital for maintaining a reliable connection, especially in high-demand situations or during unexpected disruptions.
- Improving Performance: Network impairment testing provides actionable insights into how the network can be optimised. This might involve adjusting configurations, upgrading equipment, or improving signal quality to enhance overall performance.
- Preventing Downtime: Regular testing helps catch and resolve problems before they lead to outages or degraded service. This proactive approach minimises the risk of downtime and ensures a smooth user experience.
Key Impairments to Test
Effective network impairment testing focuses on detecting specific issues that impact 5G fronthaul networks. One of the primary issues tested for is signal loss. Signal loss occurs when the strength of the signal diminishes, which can be caused by physical obstructions, interference from electronic devices, or faults in network equipment. This reduction in signal strength can result in dropped connections or degraded service quality, making it crucial to identify and address these issues.
Another significant issue is delays, also known as latency. Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another within the network. High latency can arise due to network congestion, where multiple devices or processes compete for limited bandwidth, or from poor configuration settings that slow down data transfer. Low latency is particularly important for applications that require real-time responses, such as video streaming or online gaming. Addressing latency issues helps ensure a smoother and more responsive user experience.
Testing Methods
Effective network impairment testing employs tools like network emulators and spectrum analyzers.
Network emulators simulate real-world network conditions in a controlled setting. For example, a network emulator can replicate scenarios such as heavy data traffic or network congestion to analyze the network’s response and stability. This helps identify potential issues before they affect real-world operations.
Spectrum analyzers monitor and assess the frequency spectrum used by the network. They detect signal interference and provide insights into how it impacts network performance. By examining the spectrum, sources of interference can be identified, helping to optimise network performance and ensure clear, reliable connections.
Reducing Latency
Latency and packet jitter are critical factors affecting the performance of 5G fronthaul networks, which connect baseband units (BBUs) and remote radio units (RRUs):
- Baseband Units (BBUs): BBUs are responsible for processing signals, including encoding and decoding data. They act as the central processing units of the network, handling the complex tasks required to prepare data for transmission or reception. Typically located in central data centres, BBUs manage the heavy lifting of data processing.
- Remote Radio Units (RRUs): RRUs are linked to antennas and handle the task of transmitting and receiving radio signals. They convert processed data from BBUs into radio waves and vice versa, usually positioned on cell towers or close to antennas.
Latency is the delay in data transmission between BBUs and RRUs, while packet jitter refers to variations in this delay. Both can impact network performance, affecting tasks like video streaming or online gaming.
Network emulators such as the Attero-100G are specifically designed to address these challenges by accurately simulating various network conditions, including different levels of delay and jitter. Uniquely, it maintains synchronisation integrity with its SyncE pass-through capability and external clock support, which are crucial for optimising the interaction between BBUs and RRUs. This ensures that 5G networks deliver fast, reliable service even under the most demanding conditions.
Maintaining Signal Quality
Signal quality is fundamental to network performance. Ensuring robust and clear signals involves thorough testing of both the fibre optics and signal processing systems.
Fibre Optics testing involves evaluating the integrity of the optical fibres that transmit signals. Testing checks for physical damage, such as bends or breaks, and ensures that fibre connections are clean and properly aligned. High-quality fibre optics minimise signal loss and maintain a stable connection.
Signal processing effectiveness is another critical factor. Advanced signal processing techniques, such as error correction and amplification, are employed to enhance signal quality. Testing verifies that these processes are functioning correctly and efficiently. It ensures that the signal remains accurate and free from distortions or noise that could degrade network performance.
Ongoing Monitoring
Regular monitoring is key to keeping 5G fronthaul networks efficient. Setting up real-time monitoring systems allows for quick detection and resolution of issues, helping the network stay reliable and perform well.
By focusing on these areas of network impairment testing, you can improve the efficiency of 5G fronthaul networks, ensuring they deliver the fast, reliable connectivity that users need.